|
1.實驗目的
通過編寫文件讀寫及上鎖的程序,進一步熟悉Linux中文件I/O相關的應用開發,并且熟練掌握open()、read()、write()、fcntl()等函數的使用。
2.實驗內容
在Linux中FIFO是一種進程間的管道通信機制,Linux支持完整的FIFO通信機制。
本實驗內容比較有趣,我們通過使用文件操作,仿真FIFO(先進先出)結構及生產者—消費者運行模型。
本實驗中需要打開兩個虛擬終端,分別運行生產者程序(producer)和消費者程序(customer),此時兩個進程同時對同一個文件進行讀寫操作。因為這個文件是臨界資源,所以可以使用文件鎖機制來保證兩個進程對文件的訪問都是原子操作。
先啟動生產者進程,它負責創建仿真FIFO結構的文件(其實是一個普通文件)并投入生產,就是按照給定的時間間隔,向FIFO文件寫入自動生成的字符(在程序中用宏定義選擇使用數字還是使用英文字符),生產周期及要生產的資源數通過參數傳遞給進程(默認生產周期為1s,要生產的資源總數為10個字符,顯然默認生產總時間為10s)。
后啟動的消費者進程按照給定的數目進行消費,首先從文件中讀取相應數目的字符并在屏幕上顯示,然后從文件中刪除剛才消費過的數據。為了仿真FIFO結構,此時需要使用兩次復制來實現文件內容的偏移。每次消費的資源數通過參數傳遞給進程,默認值為10個字符。
3.實驗步驟
(1)畫出實驗流程圖。
本實驗的兩個程序的流程圖如圖2.5所示。
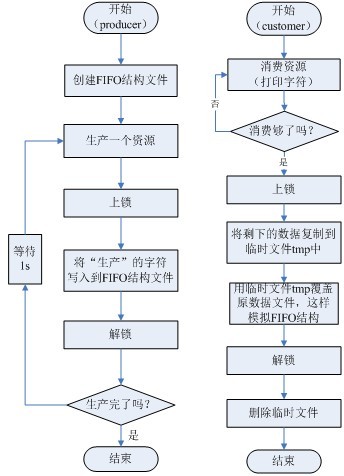
圖2.5 文件讀寫及上鎖實驗流程圖
(2)編寫代碼。
本實驗中的生產者程序的源代碼如下所示,其中用到的lock_set()函數可參見后面章節。
/* producer.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "mylock.h"
#define MAXLEN 10 /* 緩沖區大小大值 */
#define ALPHABET 1 /* 表示使用英文字符 */
#define ALPHABET_START 'a' /* 頭一個字符,可以用 'A' */
#define COUNT_OF_ALPHABET 26 /* 字母字符的個數 */
#define DIGIT 2 /* 表示使用數字字符 */
#define DIGIT_START '0' /* 頭一個字符 */
#define COUNT_OF_DIGIT 10 /* 數字字符的個數 */
#define SIGN_TYPE ALPHABET /* 本實例選用英文字符 */
const char *fifo_file = "./myfifo";/* 仿真FIFO文件名 */
char buff[MAXLEN]; /* 緩沖區 */
/* 功能:生產一個字符并寫入到仿真FIFO文件中 */
int product(void)
{
int fd;
unsigned int sign_type, sign_start, sign_count, size;
static unsigned int counter = 0;
/* 打開仿真FIFO文件 */
if ((fd = open(fifo_file, O_CREAT|O_RDWR|O_APPEND, 0644)) < 0)
{
printf("Open fifo file error\n");
exit(1);
}
sign_type = SIGN_TYPE;
switch(sign_type)
{
case ALPHABET:/* 英文字符 */
{
sign_start = ALPHABET_START;
sign_count = COUNT_OF_ALPHABET;
}
break;
case DIGIT:/* 數字字符 */
{
sign_start = DIGIT_START;
sign_count = COUNT_OF_DIGIT;
}
break;
default:
{
return -1;
}
}/*end of switch*/
sprintf(buff, "%c", (sign_start + counter));
counter = (counter + 1) % sign_count;
lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK); /* 上寫鎖 */
if ((size = write(fd, buff, strlen(buff))) < 0)
{
printf("Producer: write error\n");
return -1;
}
lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK); /* 解鎖 */
close(fd);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc ,char *argv[])
{
int time_step = 1; /* 生產周期 */
int time_life = 10; /* 需要生產的資源總數 */
if (argc > 1)
{/* 第一個參數表示生產周期 */
sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &time_step);
}
if (argc > 2)
{/* 第二個參數表示需要生產的資源數 */
sscanf(argv[2], "%d", &time_life);
}
while (time_life--)
{
if (product() < 0)
{
break;
}
sleep(time_step);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
本實驗中的消費者程序的源代碼如下所示:
/* customer.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define MAX_FILE_SIZE 100 * 1024 * 1024 /* 100M */
const char *fifo_file = "./myfifo"; /* 仿真FIFO文件名 */
const char *tmp_file = "./tmp"; /* 臨時文件名 */
/* 資源消費函數 */
int customing(const char *myfifo, int need)
{
int fd;
char buff;
int counter = 0;
if ((fd = open(myfifo, O_RDONLY)) < 0)
{
printf("Function customing error\n");
return -1;
}
printf("Enjoy:");
lseek(fd, SEEK_SET, 0);
while (counter < need)
{
while ((read(fd, &buff, 1) == 1) && (counter < need))
{
fputc(buff, stdout); /* 消費就是在屏幕上簡單的顯示 */
counter++;
}
}
fputs("\n", stdout);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
/* 功能:從sour_file文件的offset偏移處開始,
將count字節數據復制到dest_file文件 */
int myfilecopy(const char *sour_file,
const char *dest_file, int offset, int count, int copy_mode)
{
int in_file, out_file;
int counter = 0;
char buff_unit;
if ((in_file = open(sour_file, O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK)) < 0)
{
printf("Function myfilecopy error in source file\n");
return -1;
}
if ((out_file = open(dest_file, O_CREAT|O_RDWR|O_TRUNC|O_NONBLOCK, 0644)) < 0)
{
printf("Function myfilecopy error in destination file:");
return -1;
}
lseek(in_file, offset, SEEK_SET);
while ((read(in_file, &buff_unit, 1) == 1) && (counter < count))
{
write(out_file, &buff_unit, 1);
counter++;
}
close(in_file);
close(out_file);
return 0;
}
/* 功能:實現FIFO消費者 */
int custom(int need)
{
int fd;
/* 對資源進行消費,need表示該消費的資源數目 */
customing(fifo_file, need);
if ((fd = open(fifo_file, O_RDWR)) < 0)
{
printf("Function myfilecopy error in source_file:");
return -1;
}
/* 為了模擬FIFO結構,對整個文件內容進行平行移動 */
lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);
myfilecopy(fifo_file, tmp_file, need, MAX_FILE_SIZE, 0);
myfilecopy(tmp_file, fifo_file, 0, MAX_FILE_SIZE, 0);
lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK);
unlink(tmp_file);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc ,char *argv[])
{
int customer_capacity = 10;
if (argc > 1) /* 第一個參數指定需要消費的資源數目,默認值為10 */
{
sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &customer_capacity);
}
if (customer_capacity > 0)
{
custom(customer_capacity);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
(3)先在宿主機上編譯該程序,如下所示:
$ make clean; make
(4)在確保沒有編譯錯誤后,交叉編譯該程序,此時需要修改Makefile中的變量。
CC = arm-linux-gcc /* 修改Makefile中的編譯器 */
$ make clean; make
(5)將生成的可執行程序下載到目標板上運行。
4.實驗結果
此實驗在目標板上的運行結果如下所示。實驗結果會和這兩個進程運行的具體過程相關,希望讀者能具體分析每種情況,下面列出其中一種情況。
終端一:
$ ./producer 1 20 /* 生產周期為1s,需要生產的資源總數為20個 */
Write lock set by 21867
Release lock by 21867
Write lock set by 21867
Release lock by 21867
…
終端二:
$ ./customer 5 /* 需要消費的資源數為5個 */
Enjoy:abcde /* 對資源進行消費,即打印到屏幕上 */
Write lock set by 21872 /* 為了仿真FIFO結構,進行兩次復制 */
Release lock by 21872
在兩個進程結束后,仿真FIFO文件的內容如下:
$ cat myfifo
fghijklmnopqr /* a到e的5個字符已經被消費,就剩下后面15個字符 */
本文選自華清遠見嵌入式培訓教材《從實踐中學嵌入式Linux應用程序開發》
熱點鏈接:
1、linux 文件鎖的實現及其應用
2、嵌入式Linux串口應用編程之串口讀寫
3、Linux文件系統之虛擬文件系統
4、標準I/O操作函數詳解
5、標準I/O操作的緩沖存儲類型
更多新聞>> |

