 select、pselect和poll函數的區別及用法
時間:2018-09-29 來源:未知
select、pselect和poll函數的區別及用法
時間:2018-09-29 來源:未知
下面我們說一下select、pselect和poll函數的具體用法及區別
• select
對于fd_set數據類型,唯一可以進行的處理是:分配一個這種類型的變量,將這種類型的一個變量值賦給同類型的另一個變量,或對這種類型的變量使用下列4個函數中的一個:
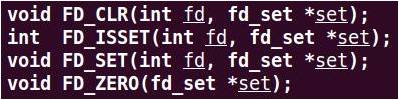
具體使用方法;
需要注意:
【1】函數的實現里面返回的話會修改timeval中的值,linux中會用剩余的時間值更新struct timeval結構,所以每次調用select都需要重新設置timeval的值。
【2】文件描述符集合也一樣,select返回的話(無論是何種方式返回)會將沒準備好的文件描述符從集合中清空,所以每次調用select函數前需要設置其文件描述符集合。
【3】當設置超時檢測時,超時了的話select返回0,如果在等待的過程中被信號中斷,那么其出錯返回-1,并且設置相應的errno而EINTR。
【4】第一個參數為大的文件描述符值(三個文件描述符集中大值)加1。因為需要的參數是文件描述符的個數,而它是從0開始編號的。
【5】所謂“準備好”,也就是說對其進行read或write操作不會阻塞,則認為其實準備好的。
【6】當socket進入select時,另一個線程調用close關掉該socket,select不能退出等待并返回。
這個行為是未指定的,man文檔中有說明
Multithreaded applications
If a file descriptor being monitored by select() is closed in another thread, the result is unspecified. On some UNIX systems, select() unblocks and
returns, with an indication that the file descriptor is ready (a subsequent I/O operation will likely fail with an error, unless another the file descriptor
reopened between the time select() returned and the I/O operations was performed). On Linux (and some other systems), closing the file descriptor in
another thread has no effect on select(). In summary, any application that relies on a particular behavior in this scenario must be considered buggy.
• pselect
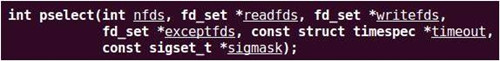
除下列幾點,select與pselect相同
1、select的超時值用timaval結構,成員為秒和微秒;pselect的超時值用timespec結構,成員為秒和納秒。
2、pselect的超時值被聲明為const,這保證了調用pselect返回后不會改變其設定的超時值。
3、pselect的后一個參數可以指定一個信號屏蔽字。如果填NULL則在于信號有關的方面select和pselect是相同的。否則,sigmask指向一有效的信號屏蔽字,在調用pselect時,以原子操作的方式安裝該信號屏蔽字,在返回時,恢復以前的信號屏蔽字。
• poll
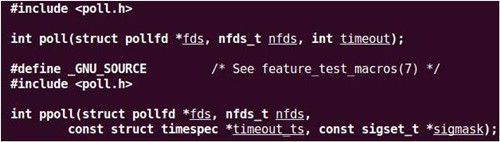
具體使用方法:
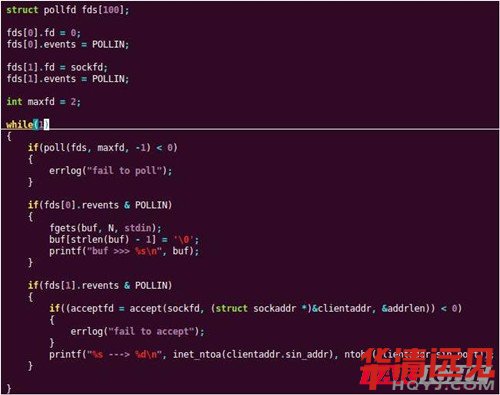
poll不會為每個條件(可讀、可寫和異常條件)構造一個描述符集,而是構造一個pollfd結構的數組,而每個數組元素指定一個描述符編號以及我們對該描述符該興趣的條件。
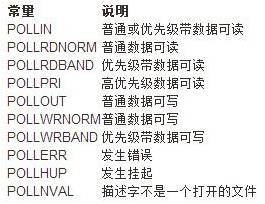
應為每個數組元素的events成員設置為下圖中值的一個或幾個,通過這些值告訴內核我們關心的是每個描述符的哪些事件。返回時,revents成員由內核設置,用于說明每個描述符發生了哪些事件。注意,poll沒有更改events成員,這與select不同。
第三個參數的精度為毫秒,如果系統不提供毫秒級精度,則timeout值取整到近的支持值。

