Fragment的使用
時間:2018-09-21 來源:未知
Fragment的使用
時間:2018-09-21 來源:未知
Fragment是Android中一個非常重要的知識,但是好多同學卻不熟悉或者根本不明白它的使用,下面我們詳細介紹一下它的使用,本次主要講解它的兩種使用方法:簡單使用和動態(tài)注冊。關(guān)于Fragment與Activity之間的通信以及生命周期方法我們下次再講解。
1.1 Fragment的使用
1.1.1 Fragment的簡單使用
這里我們準備一個簡單的Fragment的示例,在一個活動中添加兩個Fragment,并讓這兩個Fragment平分整個活動控件新建一個左側(cè)Fragment布局left ragment.xml,代碼如下所示:
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .c
om/apk /res / android "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : orientation =" vertical " >
<Button
android :id ="@+id/ button "
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
android : layout_gravity =" center_horizontal "
android : text =" Button "
/>
</ LinearLayout >
這個布局非常簡單,只是放置了一個按鈕,并讓他水平居中顯示。然后新建右側(cè)碎片布局right fragment.xml,代碼如下所示:
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .c
om/apk /res / android "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : background ="#00 ff00 "
android : orientation =" vertical " >
<TextView
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
android : layout_gravity =" center_horizontal "
android : textSize ="20 sp"
android : text =" This is right fragment "
/>
</ LinearLayout >
這里我們放置了一個TextView用于顯示文本,并將布局背景設(shè)置成綠色接著新建一個LeftFragment類,并繼承自Fragment。代碼如下:
public class LeftFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView ( LayoutInflater inflater ,
ViewGroup container , Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
View view = inflater . inflate (R. layout . left_fragment ,
container , false );
return view ;
}
}
這里重寫了Fragment的OnCreateView方法,接著調(diào)用LayoutInater的inate()方法把剛才定義的left fragment布局動態(tài)添加進來接著再新建一個RightFragment,代碼如下:
public class RightFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView ( LayoutInflater inflater ,
ViewGroup container , Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
View view = inflater . inflate (R. layout . right_fragment ,
container , false );
return view ;
}
}
接下來創(chuàng)建一個FragmentTest項目,并修改activity main.xml的代碼,如下所示:
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .c
om/apk /res / android "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent " >
<fragment
android :id ="@+id/ left_fragment "
android : name =" com . example . fragmenttest . LeftFragment "
android : layout_width ="0 dp"
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : layout_weight ="1" />
<fragment
android :id ="@+id/ right_fragment "
android : name =" com . example . fragmenttest . RightFragment "
android : layout_width ="0 dp"
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : layout_weight ="1" />
</ LinearLayout >
可以看到,我們在布局文件中使用<Fragment>
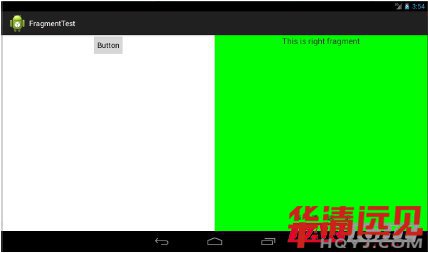
1.1.2 Fragment的動態(tài)添加
上一節(jié),我們在布局文件中進行了Fragment的添加,這一節(jié)我們在程序運行過程中把動態(tài)添加Fragment到活動中首先我們再新建一個項目,修改它的activity main.xml文件,代碼如下:
public class RightFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView ( LayoutInflater inflater ,
ViewGroup container , Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
View view = inflater . inflate (R. layout . right_fragment ,
container , false );
return view ;
}
}
接下來創(chuàng)建一個FragmentTest項目,并修改activity main.xml的代碼,如下所示:
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .com /apk /res / android "
xmlns : tools =" http :// schemas . android .com/ tools "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : paddingBottom =" @dimen / activity_vertical_margin "
android : paddingLeft =" @dimen / activity_horizontal_margin "
android : paddingRight =" @dimen / activity_horizontal_margin "
android : paddingTop =" @dimen / activity_vertical_margin "
tools : context =". MainActivity "
android : orientation =" horizontal " >
< LinearLayout
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : orientation =" vertical ">
<Button
android :id ="@+id/bt1 "
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
android : text =" fargment01 "/>
<Button
android :id ="@+id/bt2 "
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
android : text =" fragment02 "/>
<Button
android :id ="@+id/bt3 "
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
android : text =" fragment03 "/>
</ LinearLayout >
<FrameLayout
android :id ="@+id/fl"
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
>
</ FrameLayout >
</ LinearLayout >這里我們我們設(shè)置了活動界面,左邊三個按鈕豎直排列,右邊是一個FrameLayout用于顯示Fragment,當我們點擊不同的按鈕,右邊切換不同的Fragment。下面我們創(chuàng)建三個不同的Fragment類,分別設(shè)置他們的布局,代碼如下:
public class Fragment01 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView ( LayoutInflater inflater , ViewGroup container ,
Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
View v = inflater . inflate (R. layout . fragment01 , null );
return v;
}
<?xml version ="1.0" encoding =" utf -8"? >
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .com /apk /res / android "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : orientation =" vertical "
android : background ="# ff0000 ">
<TextView
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
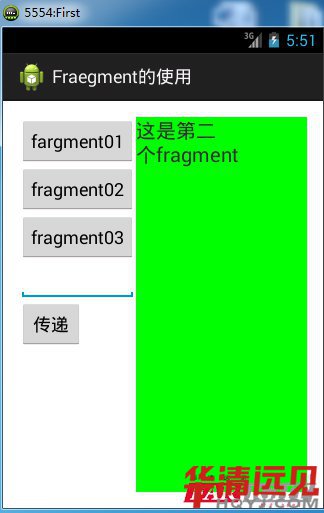
android : text這是第一個=" fragment "
android : textSize ="20 sp "/>
<EditText
android :id ="@+id/ et_frag "
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "/>
</ LinearLayout >
public class Fragment02 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView ( LayoutInflater inflater , ViewGroup container ,
Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
// TODO Auto - generated method stub
View v = inflater . inflate (R. layout . fragment02 , null );
- 4 -
return v;
}
}
<?xml version ="1.0" encoding =" utf -8"? >
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .com /apk /res / android "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : orientation =" vertical "
android : background ="#00 ff00 ">
<TextView
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
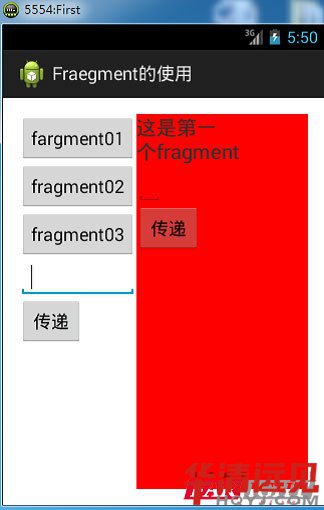
android : text這是第二個=" fragment "
android : textSize ="20 sp "/>
</ LinearLayout >
public class Fragment03 extends Fragment {
private TextView tv;
@Override
public View onCreateView ( LayoutInflater inflater , ViewGroup container ,
Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
// TODO Auto - generated method stub
View v = inflater . inflate (R. layout . fragment03 , null );
return v;
}
<?xml version ="1.0" encoding =" utf -8"? >
< LinearLayout xmlns : android =" http :// schemas . android .com /apk /res / android "
android : layout_width =" match_parent "
android : layout_height =" match_parent "
android : orientation =" vertical "
android : background ="#0000 ff" >
<TextView
android : layout_width =" wrap_content "
android : layout_height =" wrap_content "
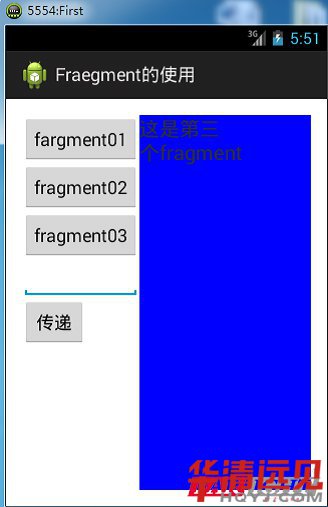
android : text這是第三個=" fragment "
android : textSize ="20 sp "/>
</ LinearLayout >
動態(tài)添加碎片主要分為5步:
1. 創(chuàng)建待添加的碎片實例。
2.獲取到FragmentManager,在活動中可以直接調(diào)用getFragmentManager()方法得到。
3. 開啟一個事務(wù),通過調(diào)用beginTransaction()方法開啟。
4. 向容器內(nèi)加入碎片,一般使用replace()方法實現(xiàn),需要傳入容器的id和待添加的碎片實例。
5. 提交事務(wù),調(diào)用commit()方法來完成。
接著在主活動中為按鈕設(shè)置點擊監(jiān)聽事件,當我們點擊按鈕后,實現(xiàn)Fragment的切換,代碼如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Fragment03 fg3 ;
@Override
protected void onCreate ( Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
super . onCreate ( savedInstanceState );
setContentView (R. layout . activity_main );
Button bt1 = ( Button ) findViewById (R.id.bt1 );
Button bt2 = ( Button ) findViewById (R.id.bt2 );
Button bt3 = ( Button ) findViewById (R.id.bt3 );
Fragment01 fg1 = new Fragment01 ();
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager ();
FragmentTransaction ft = fm. beginTransaction ();
ft. replace (R.id.fl , fg1 );
ft. commit ();
bt1. setOnClickListener (new OnClickListener () {
@Override
public void onClick ( View v) {
TODO Auto - generated method stub
Fragment01 fg1 = new Fragment01 ();
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager ();
FragmentTransaction ft = fm. beginTransaction ();
ft. replace (R.id.fl , fg1 );
ft. commit ();
}
});
bt2. setOnClickListener (new OnClickListener () {
@Override
public void onClick ( View v) {
TODO Auto - generated method stub
Fragment02 fg2 = new Fragment02 ();
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager ();
FragmentTransaction ft = fm. beginTransaction ();
ft. replace (R.id.fl , fg2 );
ft. commit ();
}
});
bt3. setOnClickListener (new OnClickListener () {
@Override
public void onClick ( View v) {
fg3 = new Fragment03 ();
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager ();
FragmentTransaction ft = fm. beginTransaction ();
ft. replace (R.id.fl , fg3 );
ft. commit ();
}
});
}
這樣就完成了在活動中動態(tài)添加Fragment的功能,運行程序,分別點擊按鈕,會在不同的Fragment之間切換